Written by: Chandrika KC, ESC Intern, VIN
Diabetes is a chronic disease which is characterized by high amount of sugar in the blood. There are two types of diabetes.
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is diabetes which is caused by problem in the endocrine system in which either pancreas does not produce enough insulin or body cannot effectively use produced insulin. Since, the function of insulin is to move glucose from the bloodstream to different cells of the body to make energy, the insufficient insulin cause glucose buildup in the blood.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: The diabetes where pancreas does not produce enough insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The diabetes where cell receptor cannot take the produced insulin.
Gestational Diabetes is the Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Insipidus is the type of diabetes which is characterized by frequent thirst and urination.
Gestational Diabetes
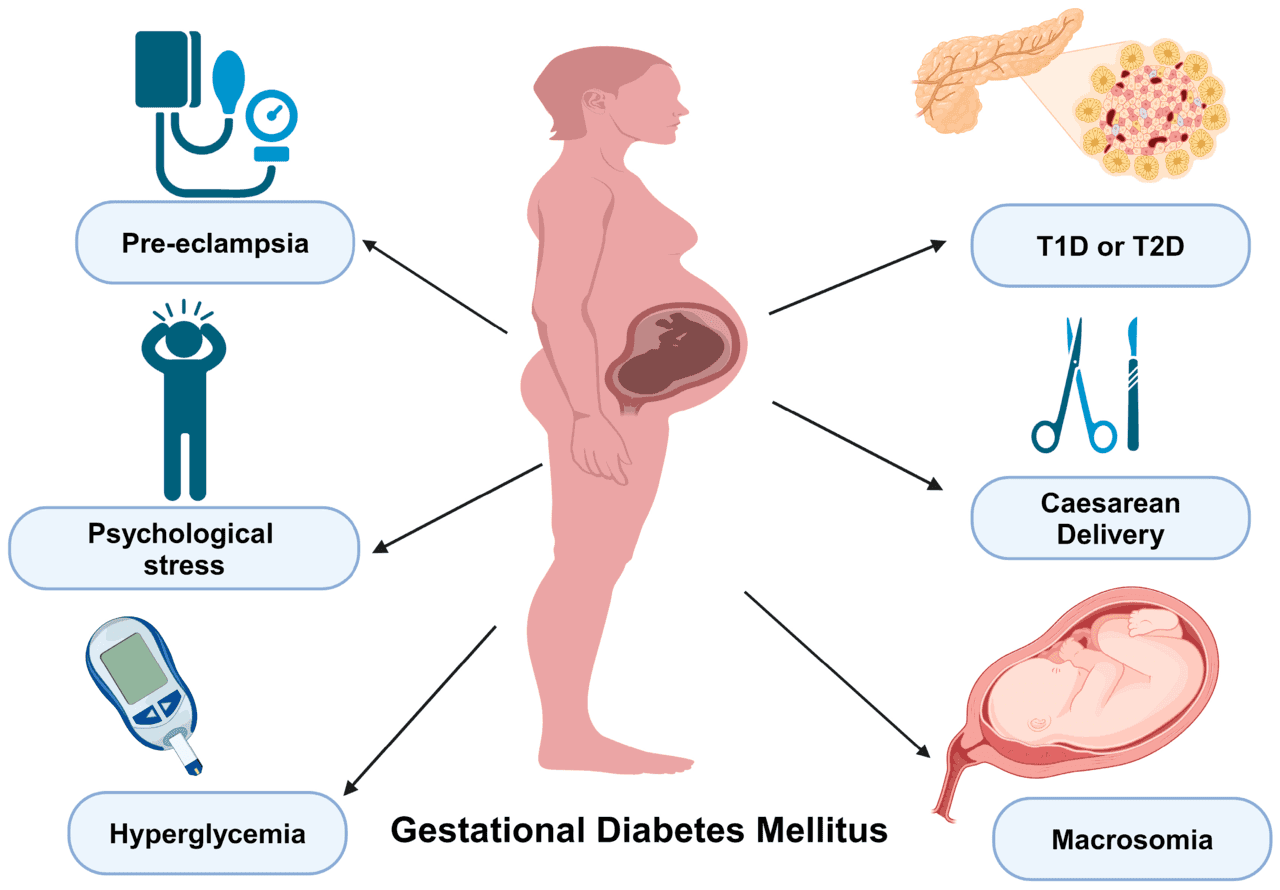
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) is the high sugar in the blood that develops during the pregnancy and disappear after giving birth.
Causes of Gestational diabetes
The causes of Gestational diabetes are not exactly known yet but the change in hormones during pregnancy may play the role in making body harder to use the insulin. It can be due to reduced insulin sensitivity in human cells, which is common in pregnant women and which is due to the progressive rising in the fetoplacental hormones such as progesterone, cortisone, growth hormone, prolactin, etc.
Risk factors of Gestational diabetes
- Obesity or overweight
- Previous history of Diabetes
- Lack of physical activities
- Having PCOS (Poly Cystic Ovarian Syndrome)
- Genetics (If parents or sibling have diabetes)
Complication caused by GDM
Maternal complication
Hypertension, Preeclampsia, urinary tract infections, polyhydramnios, future diabetes and increase operative intervention in the delivery.
Neonatal complication
Macrosomia, hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, hyperbilirubinemia, polycythemia, birth trauma, respiratory infection, etc. that increase the risk of neonatal intensive care unit admission rate.
💙 Become a Volunteer! Help us empower communities—one step at a time.
Screening and diagnosis of GDM
A 50gm oral glucose challenge test (OGCT) is widely accepted screening test for gestational diabetes mellitus. This screening is mostly done in 24 weeks to 28 weeks of gestation to the women in a non- fasting state who are at moderate risk for GDM. The women which meet or exceed the threshold 140 mg/dl received the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in which a 75gm or 100gm oral glucose load is administered in fasting state then after 1,2 and 3 hours each after the administration of glucose load.
Diagnosis criteria of GDM according to WHO 2013
| OGCT – 50 gm (after one hour) | ≥ 140 mg/dl |
| OGTT – 75 gm (fasting) | ≥ 95 mg/dl |
| 1 hour | ≥180 mg/dl |
| 2 hours | ≥ 155 mg/dl |
Medicines prescribed in GDM
The American College of Obstetrician and Gynecologist (ACOG) and American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommend the life style modification as the first line therapy for gestational diabetes. Lifestyle modifications include not only change in the diet with less or no sugar but also in physical exercise so that it can balance the hormones. However, if the glycemic control is not achieved by incorporating the lifestyle modification, insulin is medication of choice for GDM since it does not cross placenta. Alternatives to insulin is oral hypoglycemic agents like Metformin and Glyburide which is very easy to administered as compared to insulin. However, these medicine cross placenta and can be concentrated in the fetal compartment. The US Food and Drug Administration currently does not approve the oral hypoglycemic agents for the treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus.
Lifestyle modification in Gestational diabetes
Foods to eat
- Non starchy vegetables
- Broccoli, cauliflower, green leaf or spinach, green beans, etc.
- Fruits
- Eat whole fruits like apple, pears, berries and citrus fruits rather than juices.
- Proteins
- Chicken, fish, tofu, beans, lentils, etc.
- Whole grain
- Whole wheat bread, brown rice, quinoa, oats, etc.
- Dairy
- Less fat or non- fat milk, cheese, yogurt, etc.
Foods to avoid
- Sugary drinks
- Avoid sweetened drinks, juices, sodas, etc.
- Sugary snacks or foods
- Avoid sweets, candies, cakes, cookies, etc.
- Highly processed foods
- Avoid white bread, white rice and other highly refines carbohydrates.
- Fried foods
- Avoid fried foods since they are high in unhealthy fats.
- Large portion of starchy foods
- Limit the starchy foods as they contain high amount of carbohydrates.
- High- fats foods
- Limit or if possible, avoid the saturated and trans-fat.
Appropriate exercise for the pregnant women with diabetes
- Walking
- Swimming
- Low impact aerobics
- Dancing
- Light weight training
- Treadmill walking
- Bicycling
These exercises are done in the comfortability and by not forcing yourself.





